Why Pepper?
By providing a universal interface, our Pepper software makes it easy to connect POS terminals to your cash register software.
Why Pepper?
By providing a universal interface, our Pepper software makes it easy to connect POS terminals to your cash register software.
POS terminal assistant
Find out whether your terminal is supported by our solutions.
Supported POS software
Find out whether Pepper has already been integrated into your POS system.
Order a Pepper license
Ready to purchase your Pepper license?
Why Matchbox?
Matchbox automates your payment reconciliation, reduces expenditures – and turns the flood of your payment data into informative diagrams.
Free Matchbox trial
Give Matchbox a try? We would love to give you a short personal introduction and then activate your free trial account.
Supported terminal types
Find out whether your terminal is supported by our solutions.
Check now
Supported POS software
Find out whether Pepper has already been integrated into your POS system.
Check now
The driving force worth knowing
As EFT experts, we not only report on current projects here. We also like to share our knowledge about the world of cashless payments.
17 December 2020

The volume of sales in e-commerce is growing continuously. But even with regard to only stationary trade: More and more payments are made cashless. For customers, cashless payments are more convenient. But even for companies, electronic payments offer a number of advantages.
How exactly do cashless payment transactions work? Which types of cashless payment are there? What are the advantages and disadvantages for companies? And finally: What are the future trends? We will explain to you fast and simple, how cashless payment or Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) works.
Cashless payment transactions or Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT) are all kinds of electronic transactions including:
It’s always the same basic principle: By transferring essential payment data, a sum of money is moved from the payer’s bank account to the recipient’s account. These data include:
There is also a difference between the various electronic payment methods in how they transfer payment data. Here we’ll explain how the usual cashless payment methods work in (stationary) retail.
In stationary retail, a terminal reads the chip or magnetic strip stored on the cards to process the account information. The buyer authorises the transfer of the payment amount with a signature or PIN. Then the payment amount is first reserved on the buyer’s bank account, then the acquirer (or authorization) transfers the money to the seller’s account.
Here, an NFC chip (Near Field Communication) is used: In this case, there’s no need to read a chip or magnetic strip. Instead, the same information is transmitted to the payment terminal by radio using NFC.
Mobile payment applications (such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, etc.) are a form of contactless payment. With this technology, mobile end devices (often smartphones) are used to initiate, authorise and realise payments.
Apple Pay or Google Pay store the credit card data in an app, which is then accessed during the payment process. Here, too, communication with the payment terminal works via NFC.
Here, cashless payment transactions are first processed completely online via a virtual account. In the second step, this amount is debited from the linked current account or credit by direct debit.
Find out more about PayPal payments and how they can affect the posting processes of a company.
In order for cashless payment transactions to work securely and reliably, certain technical and organisational requirements must be met. This is ensured by various market players – from terminal manufacturers to payment service providers and acquirers to banks.
We will explain the key players for you.
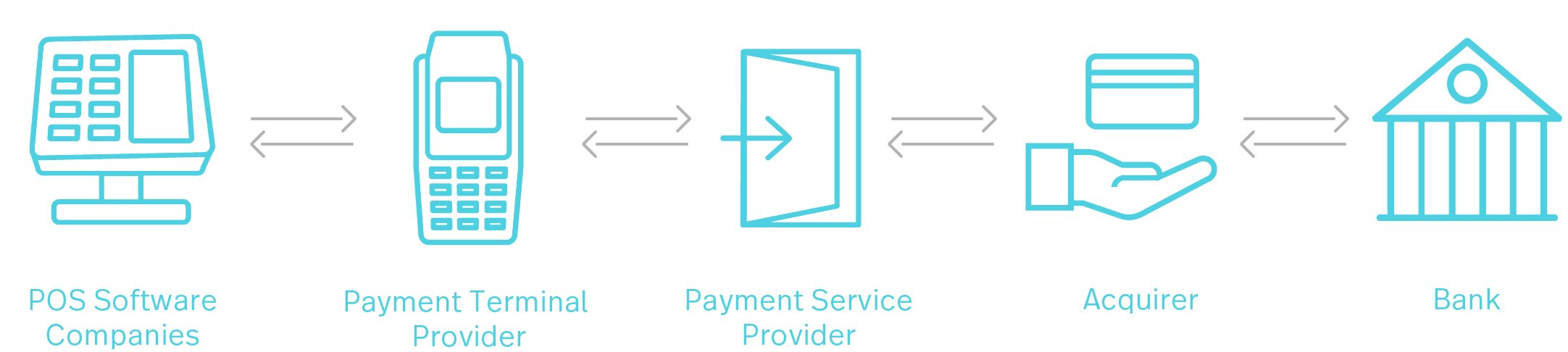
For electronic payments to work at the checkout, these systems must facilitate the processing of the various forms of payment.
Among other things, secure, reliable and fast communication between the POS systems and the payment terminals is very important. Find out here why communication may not always run smoothly – and how to master this challenge.
Payment terminals process card payments at cash registers: On the one hand, they must be able to process different types of cards and contactless payment options. On the other hand, they need to communicate with the POS systems via an interface (such as ZVT).
Especially when switching to a different terminal provider, the communication between the terminal and the cash register can quickly become problematic.But there is a solution for this, too.
Payment service providers facilitate the integration of different cashless payment methods into the company’s payment system. That way, certain credit or debit cards, online payment services or e-wallets can be accepted.
Normally, a payment service provider can use more than one acquirer or payment network, i.e. a retailer can offer many different payment methods with just one PSP. When a payment request is made, the PSP contacts the acquirer to have it confirmed or authorised.
Once a payment service provider receives a payment request, it sends the relevant information to the acquirer, who then confirms or rejects the payment based on the validity and credit limit of the card. If confirmed, the information is sent to the bank and back to the payment service provider.
The acquirer acts as a buffer between the payment service provider and the bank. Its tasks? To record, authorise and process card transactions.
The acquirer tells the bank that a payment amount has been authorised. In the next step, the bank debits the payment amount to the buyer’s account and initiates a credit note to the seller’s account.
The banks also provide bank accounts to both buyers and sellers, which are the basic requirements for the Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT).

21 March 2024 – What do you actually do with your expired debit cards, credit cards and railcards? They’re simply too good to throw away. If you want to quickly make something practical, surprise your colleagues or bring a little light relief to your next customer meeting, we’ve got three upcycling ideas for ... Continue reading

7 December 2023 – «For us Pepper works like a universal adapter, which makes it vastly easier to connect different terminal types», says Rüdiger Boesen, Product Management TCPOS at Zucchetti, summarising his understanding of the software. A general contract was consequently concluded for the DACH region back at the start of the 2000s. Continue reading

4 December 2023 – Having already worked with treibauf for some time, Bächli Bergsport is now also using automated payment reconciliation from Matchbox for its accounting. Discover the motivation behind the company’s decision – and what’s changed since the rollout. Continue reading